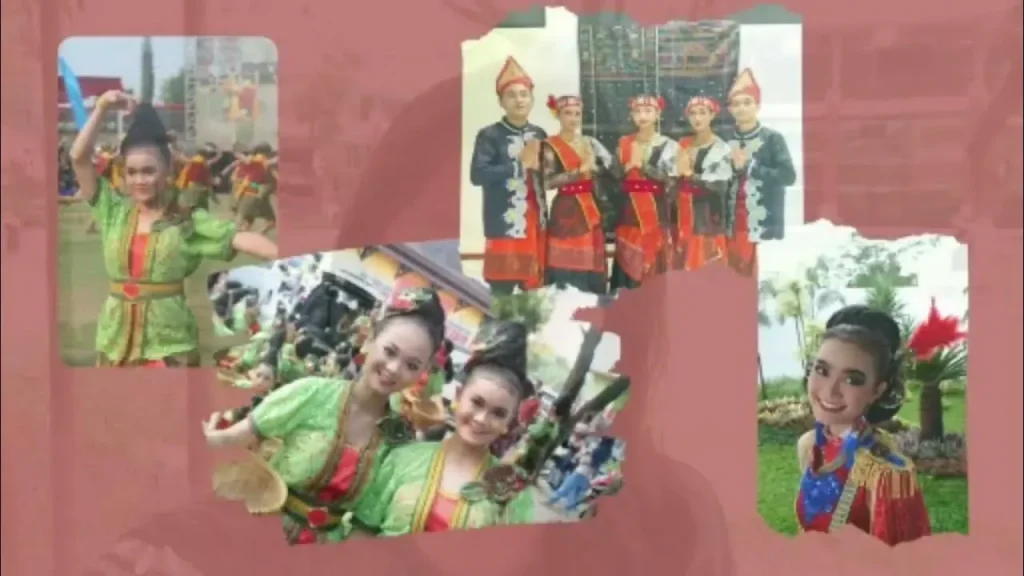
Preserving culture in the 21st century is a dynamic, ongoing mission that blends reverence for the past with openness to new ideas. To succeed, communities must navigate balancing tradition and modernity as they adopt technologies, share stories online, and welcome diverse voices. This process relies on cultural preservation that protects languages, crafts, rituals, and knowledge while allowing living practices to evolve. It also reinforces cultural identity in modern society, helping people feel connected to roots even as daily life changes. By recognizing heritage protection in the digital era and supporting intangible cultural heritage, societies can nurture resilience, creativity, and inclusive growth.
Seen from another lens, safeguarding living traditions in a connected world means protecting cultural memory for tomorrow’s generations. This perspective emphasizes active participation, intergenerational knowledge transfer, and authentic storytelling rather than passive display. Applying Latent Semantic Indexing principles, we can pair terms such as heritage conservation, intangible heritage, cultural continuity, and digital stewardship to broaden the conversation. Ultimately, the aim is to nurture identity and creativity in contemporary life while honoring origins and community agency.
Preserving culture in the 21st century: Balancing tradition and modernity for cultural preservation and identity
Preserving culture in the 21st century is a dynamic, ongoing process that requires thoughtful navigation of how communities honor enduring customs while adapting to rapid technological, economic, and social changes. The practice hinges on balancing tradition and modernity in ways that respect roots without stifling innovation. By consciously weaving old practices into contemporary life, communities can maintain a living archive—an evolving repository of knowledge, skills, and expressions that sustains cultural preservation while remaining relevant to today’s realities.
To truly advance cultural preservation, it is essential to place culture at the center of public life and policy, recognizing its role in shaping identity and resilience. This involves fostering cultural identity in modern society by encouraging intergenerational dialogue, education, and community-driven initiatives that keep traditions alive while embracing new forms of expression. When preservation becomes a living, participatory process, it supports living practices that communities use to navigate the modern world and connect with others across borders.
Intangible cultural heritage in the digital era: safeguarding heritage protection in the digital era while nurturing cultural identity in modern society
Intangible cultural heritage thrives when communities actively safeguard heritage protection in the digital era while adapting to digital platforms that broaden access and participation. Technology can democratize learning, enabling tutorials, storytelling, and knowledge-sharing that transmit skills—from song or craft to ceremonial practices—across generations. Yet, the same tools can threaten authenticity if symbols and meanings are misunderstood or commodified, making careful curation and community verification essential to preserve the emotional and relational dimensions that breathe life into living traditions.
Strategies for safeguarding intangible cultural heritage include documentation, archiving, and ethical engagement with heritage. By recording oral histories, recipes, and techniques, communities create accessible resources that reach wider audiences without compromising context. This approach also reinforces cultural preservation by anchoring modern audiences to the values and rituals that form a core part of cultural identity in modern society. Through respectful partnerships, public support, and ongoing education, heritage protection in the digital era can coexist with vibrant, evolving expressions of culture.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can communities pursue preserving culture in the 21st century by balancing tradition and modernity?
Communities can pursue preserving culture in the 21st century by actively balancing tradition and modernity through intergenerational collaboration, education, and community programming. Emphasize cultural preservation by documenting living practices, teaching local languages, and supporting heritage events that invite participation from all ages. Use digital storytelling and responsible adaptation to keep intangible cultural heritage relevant while honoring origins. This balanced approach sustains identity and resilience in modern society.
What strategies support heritage protection in the digital era to safeguard intangible cultural heritage and cultural identity in modern society?
Strategies include documenting and archiving living practices through accessible digital collections, open archives, and language resources. Implement community-led verification and context-rich explanations to protect intangible cultural heritage from misrepresentation. Promote ethical engagement, co-creation with communities, and transparent governance to reinforce cultural identity in modern society. Combine public and private funding with supportive policies to sustain heritage protection in the digital era while enabling innovation.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic, ongoing preservation | Preserving culture in the 21st century is a living process that balances longstanding customs with rapid technological, economic, and social changes. |
| Value of cultural preservation | Culture provides identity and resilience; preservation keeps living practices alive as a resource for education and inspiration for future generations. |
| Balancing tradition and modernity | Tradition offers continuity, while modern life offers inclusion and innovation. The aim is to adapt where appropriate without losing roots. |
| Digital era challenges | Digital exchange can risk misinterpretation or commodification, but technology also broadens access and participation in cultural expressions. |
| Globalization pressures | Global ideas can erode local languages and crafts; heritage protection in the digital era is essential to safeguard intangible cultural heritage. |
| Strategies for sustaining culture | Intergenerational collaboration; education integration; documentation and archiving; community programming; language revival; ethical engagement; policy/funding; responsible tourism; support for intangible heritage. |
| Role of technology | Tech can democratize access and preservation, but requires community verification and contextualization to avoid superficial representations. |
| Path forward | A democratic, ongoing process that sustains identity, creativity, and connection through balanced, thoughtful change. |
Summary
Consequently, preserving culture in the 21st century hinges on a collaborative approach that values living practices, protects intangible heritage, and leverages digital tools to educate and connect communities while honoring local identities.