Liver disease is a silent epidemic affecting millions, often without clear symptoms until it’s too late. Conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) have surged in prevalence as obesity rates climb, making awareness and liver health critical issues. These diseases can lead not only to significant liver damage but also greatly increase the risk of liver cancer, often sneaking up without warning. With one in five individuals living with MASLD, understanding its implications and pursuing early diagnosis is vital for maintaining optimal liver health. As we delve deeper into the factors contributing to liver disease, we uncover the importance of lifestyle choices and their long-lasting impact on our well-being.
Liver disorders, often referred to in the medical community as hepatic diseases, encompass a variety of conditions that can jeopardize overall health. Among these, the rise of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, or MASLD, has drawn considerable attention due to its link with lifestyle factors like diet and weight management. Such hepatic conditions not only affect organ function but also serve as precursors to more severe health risks, including liver cancer. Understanding these terms and their implications is essential in navigating the complexities of liver health. As we confront the growing trend of liver-related issues, the call for proactive health measures becomes increasingly urgent.
Understanding Liver Disease: What You Need to Know
Liver disease encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the liver’s health and functionality. This organ plays a crucial role in processing nutrients, filtering toxins, and serving as a metabolic powerhouse. Among various liver ailments, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming increasingly prevalent, especially in populations leading sedentary lifestyles. Unlike traditional liver diseases associated with alcohol consumption, NAFLD is often linked to obesity and metabolic conditions, making awareness of its risk factors essential.
The lack of obvious symptoms in liver diseases such as NAFLD can be deceptive, leading many to underestimate the importance of liver health. Individuals often misattribute feelings of fatigue and lethargy to their lifestyle or work stress, overlooking the potential underlying issues related to the liver. Engaging in conversations about liver disease and understanding the implications of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) can play a vital role in early detection and prevention of more severe liver complications.
The Rise of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
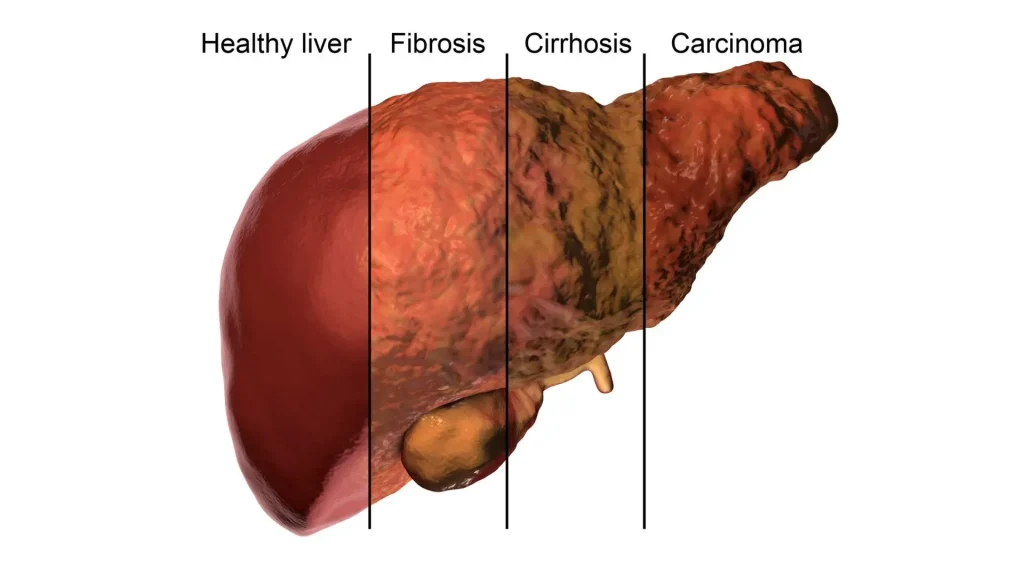
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has emerged as a significant health concern globally, with one in five individuals being affected according to The British Liver Trust. Characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver not caused by alcohol consumption, NAFLD can often go undetected until it’s too late. The rise of unhealthy diets, particularly those high in sugar and fats from ultra-processed foods, has been linked to this alarming increase. People unaware of their liver health may unknowingly contribute to their risk of developing conditions like cirrhosis or even liver cancer.
Health professionals agree that lifestyle choices significantly influence the progression of NAFLD. Incorporating balanced nutrition and regular physical activity can mitigate risk factors associated with the disease. Furthermore, as insights grow regarding the link between obesity and liver health, healthcare providers emphasize the importance of preventive screenings for those at risk. Detecting NAFLD early, especially in adults suffering from conditions like diabetes, can lead to effective management and healthier outcomes.
Impact of MasLD on Public Health
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), as a more progressive form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is being recognized as a leading cause of liver-related health issues. In the UK, the increasing incidence of MASLD correlates with rising obesity rates, underlining the importance of addressing not just liver health but also associated metabolic disorders. As MASLD can lead to complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, public health initiatives are now focusing on awareness and education to help combat this silent epidemic.
The statistics surrounding MASLD are particularly alarming, with estimates suggesting that around 15 million people in the UK are affected, often without even realizing it. This underscores the critical need for healthcare providers to engage patients in discussions about metabolic syndrome and its implications for liver disease. Ongoing research into the direct correlations between MASLD and liver cancer risk is showing that diligent monitoring and lifestyle interventions could significantly reduce the burden of liver disease on public health.
Lifestyle Changes for Liver Health
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can dramatically improve liver health and reduce the risks associated with conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Key changes often involve dietary modifications—reducing intake of sugars and ultra-processed foods while increasing consumption of nutrient-dense options like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can facilitate better liver function. For example, substituting processed sauces with homemade alternatives can significantly reduce hidden fats and sugars, enhancing overall well-being.
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity plays an essential role in maintaining healthy liver function. Engaging in exercises that promote cardiovascular health can aid in weight management and curb the accumulation of fat in the liver. Incorporating routine checks and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers is crucial—especially for individuals at risk of liver disease. Embracing these lifestyle changes not only safeguards liver health but also promotes a holistic approach to overall wellness.
The Link Between Obesity and Liver Disease
Obesity has been identified as a significant risk factor for developing liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its advanced form, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). The accumulation of excess fat in the liver can disrupt its normal functions, leading to inflammation and scarring over time. Experts warn that as obesity rates continue to rise, particularly among younger populations, the prevalence of liver disease will likely follow suit.
This relationship between obesity and liver disease emphasizes the importance of awareness and proactive health measures. Tackling obesity through education about nutrition and the benefits of physical activity is crucial for limiting the risk of developing liver conditions. Furthermore, addressing misconceptions about liver health, particularly the misconception that only alcohol consumption leads to liver damage, is essential in promoting healthier lifestyle choices across the community.
Signs and Symptoms of Liver Disease
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of liver disease can be challenging, as many individuals with conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) experience few or no noticeable symptoms until the disease has progressed. Common early symptoms may include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight gain. This lack of observable symptoms often results in delayed diagnosis, underscoring the necessity for regular check-ups and screenings.
As liver disease advances, more significant symptoms may emerge, including jaundice, persistent itching, and an increase in liver size. Unfortunately, by the time these symptoms appear, the liver may already be severely compromised. Medical professionals stress the need for individuals to be proactive about their liver health through lifestyle modifications and routine monitoring, ensuring that any potential issues are identified and addressed early.
Understanding Liver Cancer Risk
The link between liver disease and liver cancer risk is a growing concern in modern medicine. Conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its advanced stage, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), have been identified as significant risk factors for developing liver cancer. With the emergence of studies indicating a rise in liver cancer rates among younger individuals, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, understanding these connections is critical for prevention and early detection.
Early intervention and lifestyle changes can help lower the risk of progression from liver diseases to cancer. Healthcare providers advocate for regular screenings for individuals at risk, along with educating patients about the importance of weight management, diet, and physical activity in maintaining liver health. Through awareness and proactive health measures, the instances of liver cancer related to underlying liver conditions can potentially be reduced.
The Role of Diet in Liver Health
Diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining liver health, especially in the context of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). High-consumption foods, particularly ultra-processed items loaded with sugars and unhealthy fats, can directly impact liver functionality, leading to fat accumulation and inflammation. Therefore, focusing on a balanced and nutrient-rich diet is fundamental to preventing liver disease and promoting overall well-being.
Incorporating whole foods, such as fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, fosters a healthier liver. Moreover, educating individuals on reading labels and understanding hidden sugars in commercially prepared foods empowers better dietary choices. Encouraging a culinary culture that prioritizes fresh, unprocessed ingredients can significantly contribute to improving liver health and preventing diseases related to metabolic dysfunction.
The Importance of Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings play a crucial role in the early detection and management of liver disease. For individuals at risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), proactive monitoring can aid in identifying changes in liver health before they escalate into serious conditions. Many people may dismiss the significance of liver health due to a lack of obvious symptoms; however, regular check-ups can uncover underlying issues that require immediate attention.
Emphasizing the importance of health check-ups, professionals advocate for routine liver function tests and consultations, especially for those with risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, or a family history of liver disease. Implementing these strategies can enhance awareness and facilitate early intervention, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a prolonged quality of life. Encouraging individuals to prioritize their liver health through screening is a significant step toward combatting the rising rates of liver disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver of individuals who consume little to no alcohol. It is largely linked to obesity, diabetes, and poor diet. NAFLD can progress to more serious liver problems, making early diagnosis and lifestyle changes crucial for liver health.
How is liver health affected by lifestyle choices?
Liver health is significantly influenced by lifestyle choices such as diet, exercise, and alcohol consumption. A diet high in processed foods and sugars can lead to conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), increasing the risk of inflammation and liver damage.
What are the risks associated with MASLD?
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) increases the risk of serious liver issues, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. It occurs when excess fat disrupts liver function, leading to inflammation and potentially scarring. Early intervention through lifestyle changes is vital to prevent progression and improve liver health.
What lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of liver cancer related to liver disease?
To reduce the risk of liver cancer linked to liver disease, focus on maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods while minimizing processed foods and sugars. Monitoring liver health through regular screenings can help detect conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) early.
How can I assess my liver health?
To assess your liver health, consult a healthcare provider for regular screenings and imaging tests like ultrasounds. Blood tests can also check liver enzymes and markers of liver health. Individuals at risk, particularly those with obesity or diabetes, should monitor for symptoms related to NAFLD and MASLD regularly.
What diet is recommended for improving liver health?
For improving liver health, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is recommended. Avoid ultra-processed foods and limit sugar intake, as these can contribute to conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Staying hydrated and reducing consumption of alcohol also benefits liver function.
Can liver disease be reversed?
In some cases, liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), can be reversed with lifestyle changes such as weight loss, improved diet, and regular exercise. Early diagnosis and proactive management are key to restoring liver health and preventing further complications.
What symptoms should I be aware of regarding liver disease?
Liver disease often presents with few initial symptoms. However, signs to watch for include fatigue, unexplained weight loss, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and abdominal discomfort. Conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) may be asymptomatic until more advanced stages, making regular monitoring important.
Who is at risk of developing liver disease?
Individuals most at risk of developing liver disease include those who are overweight, have diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or a high alcohol intake. Additionally, those with poor dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic predispositions may also be more susceptible to liver conditions such as NAFLD and MASLD.
How serious is liver cancer related to liver disease?
Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a serious complication that can arise from liver diseases like cirrhosis and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). The silent progression of liver disease emphasizes the importance of early detection and management to prevent this potentially fatal condition.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Adam Wereszczynski’s Diagnosis | At 36, Adam was diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which he discovered after a health scare. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Adam’s busy lifestyle involved frequent dining at upscale restaurants and a diet high in rich foods, often unaware of hidden fats. |
| Symptoms and Awareness | Common symptoms are often unnoticeable, making it crucial to raise awareness about liver health and potential risks. |
| Statistics on Masld | MASLD (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease) affects 15 million individuals in the UK, highlighting the need for early diagnosis. |
| Impact of Diet | High consumption of ultra-processed foods and hidden fats contributes directly to liver stress and potential disease. |
| Adam’s Transformation | After treatment and lifestyle changes, Adam lost 28 pounds and improved his liver health, feeling more energized and healthy. |
Summary
Liver disease is a growing concern affecting millions globally, with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) becoming increasingly prevalent. Adam Wereszczynski’s story exemplifies the hidden risks associated with modern lifestyles, where busy work schedules and the tendency to indulge in rich foods can lead to serious health complications. Awareness and proactive measures are essential to prevent this silent disease, which can pave the way for more severe liver conditions if left unchecked. By prioritizing liver health through lifestyle changes and understanding underlying risks, individuals can significantly improve their overall well-being.