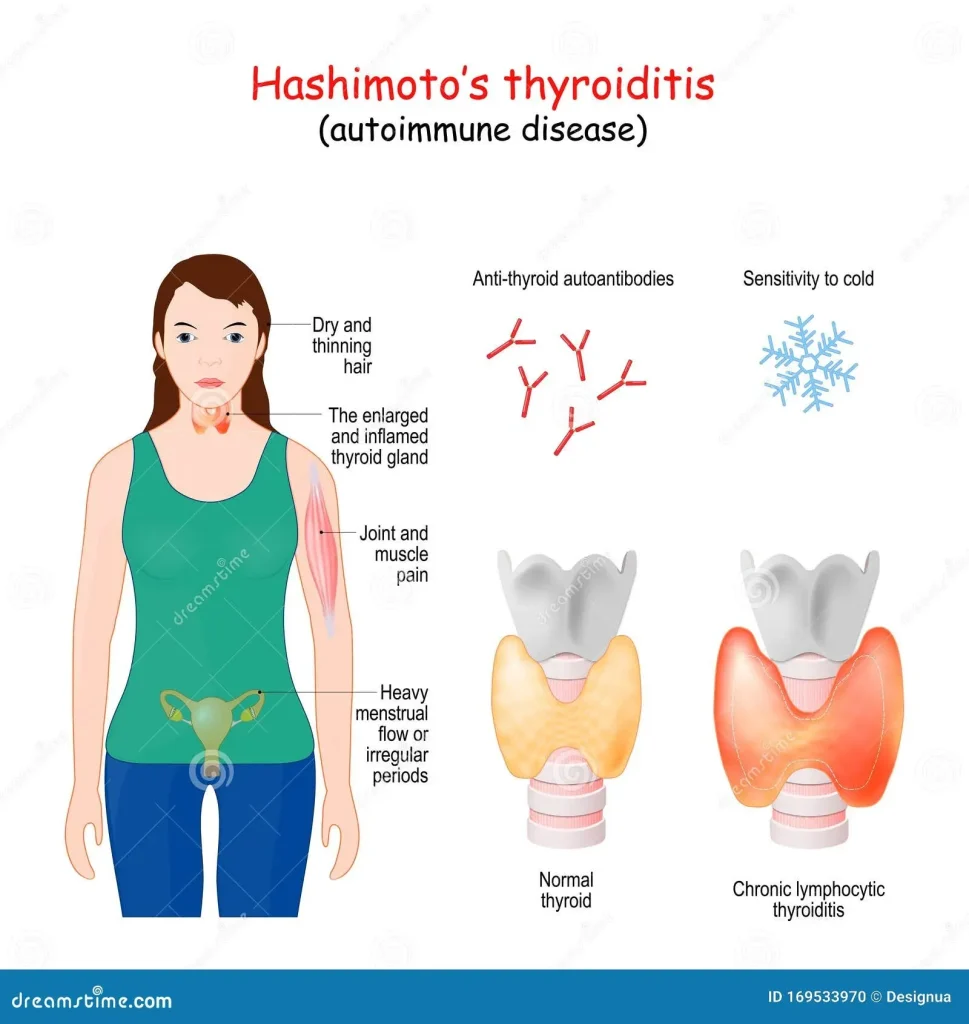
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a prevalent autoimmune disease that affects many individuals, leading to various thyroid problems such as hypothyroidism. Characterized by the body’s immune system attacking the thyroid gland, individuals diagnosed often experience debilitating symptoms including extreme fatigue and unexpected weight gain. This condition is particularly common among women and can go undiagnosed for years, impacting overall quality of life and energy levels. Many people, like Hannah, may mistakenly attribute their symptoms to stress from work or family responsibilities, unaware that an underlying thyroid condition is at play. Understanding Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is essential not only for improving personal health but also for addressing the broader issue of how autoimmune diseases can complicate everyday life.
The term Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is sometimes referred to as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis or simply autoimmune thyroid disease. Often confused with other forms of thyroid dysfunction, this condition leads to insufficient hormone production from the thyroid, resulting in symptoms like weight fluctuations, persistent fatigue, and decreased metabolic function. As a leading cause of hypothyroidism, it highlights the importance of recognizing the symptoms and obtaining appropriate medical tests to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. With many individuals experiencing a lack of awareness about their underlying health issues, exploring alternative terms can further illuminate the discussions surrounding this critical health concern.
Understanding Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: The Silent Struggle
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a prevalent autoimmune disease that strikes at the heart of our body’s metabolic processes. By launching an attack on the thyroid gland, it can lead to a significant decline in thyroid hormone production, ultimately resulting in hypothyroidism. This condition is particularly insidious; many patients, like Hannah, spend years grappling with unexplained fatigue, weight gain, and overall malaise without a proper diagnosis. Symptoms can be so vague and varied that they can often be mistaken for normal life stresses, especially for busy professionals and parents managing multiple responsibilities.
Historically, the intersection of autoimmune diseases and everyday life is not often discussed in mainstream health narratives. However, understanding Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is crucial, as it provides insight into how many individuals may be unknowingly suffering. The connection between thyroid problems and lifestyle changes is critical, as fatigue can be compounded by factors such as parenting and demanding careers, leading to an alarming increase in these cases going undiagnosed. Knowing the signs—like severe fatigue, unexplained weight gain, and persistent cold intolerance—may help more people recognize their symptoms rather than accepting them as a normal part of busy life.
The Impact of Hypothyroidism on Daily Life
Living with hypothyroidism can be remarkably challenging, as seen in Hannah’s experiences. The condition doesn’t merely cause physical symptoms; it can deeply affect mental and emotional health too. Individuals often report feeling an overwhelming sense of fatigue, such that even the simplest daily tasks become monumental challenges. As metabolism slows, people may encounter strange weight fluctuations despite maintaining a consistent diet and exercise regimen, which can lead to frustration and helplessness.
Moreover, the mental fog associated with hypothyroidism can impact cognitive function, making it difficult to concentrate and complete professional tasks effectively. This can compound existing stress, leading to a vicious cycle where fatigue worsens due to job-related pressures and home life demands. Recognizing these cumulative effects is essential for both patients and their supports systems to foster understanding and seek appropriate treatment paths, ultimately enhancing quality of life.
How Autoimmune Diseases Affect Metabolism
Autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can disrupt the delicate balance of hormonal and metabolic functions in the body. The thyroid gland is a key player in regulating metabolism, and when it is compromised, as in the case of hypothyroidism, the effects can result in a cascade of complications. With thyroid dysfunction, energy levels plummet, leading to weight gain that feels uncontrollable. The metabolic slowdown can be so profound that even small calorie reductions seem futile, perpetuating a cycle of frustration for those affected.
This hormonal imbalance can also lead to difficulties in maintaining a healthy weight, as individuals find that traditional methods of weight loss—dietary modifications and exercise—yield minimal results. Understanding how thyroid health interlinks with metabolic function highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. By managing thyroid hormone levels through medication like levothyroxine, individuals can restore some metabolic functions and develop effective weight management strategies.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Recognition of hypothyroidism symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can range widely, often presenting differently in patients. For people like Hannah, extreme fatigue, weight gain, hair thinning, and a heightened sensitivity to cold can be significant warning signs. Unfortunately, many individuals dismiss these symptoms as a byproduct of a busy lifestyle, leading to delayed interventions that could improve their quality of life. Symptoms such as difficulty concentrating and constant tiredness are particularly pressing in the context of daily responsibilities, impacting both personal and professional life.
By raising awareness of these symptoms, healthcare professionals can better assist in identifying patients who may be struggling with these often-overlooked conditions. Moreover, creating accessible platforms for discussing these issues in public forums could empower more individuals to seek help rather than simply adjusting their lifestyle to accommodate what they perceive as normal fatigue or stress. Encouraging open discussions about thyroid health can lead to quicker diagnoses and improved overall wellness for many.
Thyroid Health: The Role of Diet and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a critical role in thyroid health, particularly for those diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and hypothyroidism. A diet rich in essential nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc can significantly support thyroid function and improve overall wellbeing. Conversely, the consumption of highly processed foods, which may contain additives and preservatives, can exacerbate symptoms and hinder recovery. Individuals must be educated on choosing whole, nutrient-dense foods that can aid in managing their symptoms and supporting hormonal stability.
Moreover, for those with autoimmune diseases, a potential focus on anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate some of the adverse effects associated with the condition. Incorporating whole grains, healthy fats, and a diverse array of fruits and vegetables can support thyroid function and balance hormones. Working with a nutritionist experienced in thyroid health can provide tailored dietary plans that address deficiencies while promoting a healthy metabolism—essential for managing weight gain and fatigue associated with these conditions.
Finding the Right Treatment for Thyroid Disorders
Navigating the treatment landscape for thyroid disorders can be complex, but it is crucial for those suffering from conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Medications such as levothyroxine are standard for managing hypothyroidism, but finding the right dosage can take time. Patients often describe the emotional journey of adjusting to medication, experiencing a rollercoaster of symptoms as they work closely with their healthcare providers to stabilize hormone levels. This iterative process underscores the necessity for ongoing communication between patients and doctors.
Furthermore, comprehensive care means considering additional treatments beyond medication. Lifestyle changes, such as dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, are integral components of an effective management strategy for thyroid conditions. Establishing a holistic approach helps patients regain control over their health and fosters a deeper understanding of their conditions. This empowered perspective is vital for long-term health and wellbeing, as it enables individuals to navigate the ups and downs of living with thyroid diseases.
The Emotional Toll of Living with Hashimoto’s
The emotional impact of living with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can be profound. Many individuals endure challenges related to body image, especially due to the weight fluctuations often experienced. As symptoms manifest and worsen over time, it can produce a profound sense of frustration and guilt, especially when traditional methods of weight loss seem ineffective. Patients may feel isolated, believing they are alone in their struggles, leading to potential mental health repercussions such as anxiety and depression.
Recognizing and addressing the emotional aspects of living with an autoimmune disease is critical. Support groups and therapy can offer individuals a safe space to discuss their emotions and experiences. Many find solidarity and understanding within segments of their community that share similar journeys, reinforcing the idea that they are not battling their condition alone. Cultivating an open dialogue about the emotional toll of these conditions can empower patients to seek the help they need, fostering a better quality of life overall.
Living with Autoimmune Diseases: Hannah’s Journey
Hannah’s experience with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis illustrates the profound effects of autoimmune diseases on everyday life. From grappling with extreme fatigue to facing significant weight gain, her journey reflects the struggles many face when dealing with undiagnosed thyroid issues. The turning point for Hannah occurred when she finally received her diagnosis, marking a shift in her life as she began treatment. The relief of understanding the root cause of her symptoms was monumental and propelled her toward a journey of healing and reclaiming her vitality.
Her success following treatment, marked by significant weight loss and increased energy levels, serves as a beacon of hope for others who might be stuck in similar struggles. By sharing her story, Hannah highlights the importance of advocating for oneself in medical spaces, encouraging others to seek answers when their symptoms feel dismissed. Such personal testimonies contribute to a wider conversation about autoimmune diseases, nurturing awareness and understanding in a world where many live in the shadows of their conditions.
The Importance of Family History in Thyroid Conditions
Family history plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Genetic predisposition often influences the likelihood of developing thyroid disorders, making it vital for patients to share their family health patterns with their healthcare providers. In Hannah’s case, discovering that family members also suffered from similar conditions helped inform her treatment plan and emphasized the familial nature of the disease.
Understanding the hereditary aspects of thyroid conditions can guide families in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate testing and management. This proactive approach can lead to a higher rate of diagnosis and a quicker path to treatment, mitigating potential complications that may arise from untreated hypothyroidism. By emphasizing the connection between family health histories and autoimmune disease management, healthcare providers can better serve their patients, fostering a community-oriented approach to healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and how does it relate to thyroid problems?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid. This condition affects the gland’s ability to produce hormones that regulate metabolism, which can result in fatigue and unexplained weight gain.
How can Hashimoto’s thyroiditis cause weight gain?
Individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis often experience a slowed metabolism due to reduced thyroid hormone production. This slowdown means that fewer calories are burned at rest, making it easy to gain weight, even with standard dietary habits and exercise.
What are the common symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Common symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis include extreme fatigue, unexplained weight gain, difficulty concentrating, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, and constipation. Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for managing this autoimmune disease effectively.
How is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis diagnosed?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is diagnosed through blood tests that measure levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones. An elevated TSH level, along with low levels of free thyroxine (fT4), indicates hypothyroidism caused by Hashimoto’s.
What treatment options are available for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
The primary treatment for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the daily use of levothyroxine, a synthetic hormone that replaces the lack of thyroid hormones in the body. With proper management, patients can regain energy levels and manage their weight effectively.
Can Hashimoto’s thyroiditis lead to other health issues?
If left untreated, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can lead to complications such as high cholesterol, heart disease, and an increased risk of other autoimmune diseases. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent these potential health issues.
What dietary considerations should people with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis be aware of?
Individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis may benefit from a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc, which support thyroid health. It’s also important to avoid excessive consumption of goitrogens found in raw cruciferous vegetables, which can interfere with thyroid function.
Is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis hereditary?
Yes, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can run in families. Genetic predisposition is a significant factor, as about 50% of individuals with the condition have a family history of thyroid problems or other autoimmune diseases.
How does Hashimoto’s thyroiditis affect mental health?
Many individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis experience symptoms such as fatigue and brain fog, which can negatively impact mental health, leading to feelings of depression or anxiety due to the chronic nature of the disease and its symptoms.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Adopting a lifestyle that includes regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and a healthy diet can significantly help manage the symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and improve overall well-being.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis | Hannah was diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis after years of unexplained fatigue and weight gain. |
| Symptoms of Hashimoto’s | Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, difficulty concentrating, intolerance to cold, constipation, and dry skin. |
| Impact on Metabolism | The condition causes a slowdown in metabolism, making weight loss difficult and weight gain easy. |
| Treatment | Patients often receive synthetic thyroid hormone (e.g., levothyroxine) to manage symptoms. |
| Family History | Hashimoto’s often runs in families, and genetic factors may contribute to its development. |
| Emotional & Social Effects | The condition can lead to feelings of embarrassment and frustration regarding weight and fatigue. |
Summary
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a significant autoimmune disorder that leads to weight gain and extreme fatigue due to an underactive thyroid gland. Understanding Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is crucial for those experiencing unexplained weight changes or persistent tiredness, as early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms effectively. With appropriate medical intervention, like synthetic hormone therapy, patients can regain their energy levels and improve their quality of life.