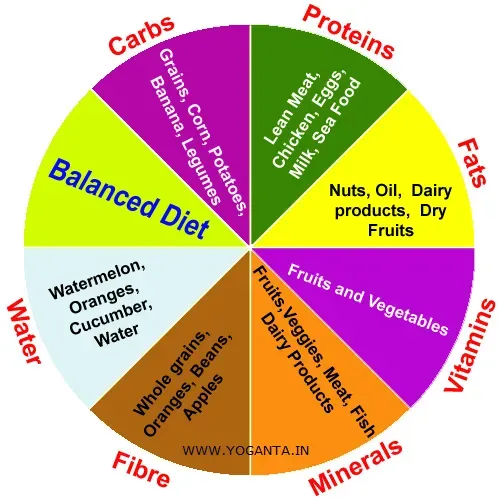
Balanced Diet Principles establish a practical framework for lasting health, emphasizing variety, moderation, and mindful eating. Nutrition for health is built on steady habits rather than quick fixes, guiding you toward sustainable changes. By focusing on a plate-balanced approach, fiber, protein, and healthy fats, you can simplify meal planning and enjoy every bite. These principles support energy, mood, and long-term wellness by promoting balanced portions and regular hydration. With practical tips on portion control, whole foods, and avoiding ultra-processed items, you can turn knowledge into lasting healthy eating habits.
Using alternative terms like a nutrient-balanced approach or a healthy-eating framework helps you see the topic from new angles without losing the core message. A diet of varied plant and animal foods, attention to portion sizes, and energy alignment with activity creates a steady path toward wellness. This LSI-inspired framing invites connections to related ideas such as meal planning, mindful eating, and energy balance, enriching the search relevance. In practical terms, the concept centers on real foods, adequate fiber, and moderate portions that fit your culture and daily schedule.
Balanced Diet Principles: A Practical Path to Nutrition for Health
Balanced Diet Principles offer a practical path to nutrition for health. By emphasizing variety, adequacy, and moderation, you nourish your body with nutrient-dense foods while avoiding extremes. This approach aligns with nutrition for health goals by supporting steady energy, mood, and long-term wellness. It also complements strategies like meal planning and portion control, turning daily eating into a sustainable pattern rather than a set of fleeting fixes.
Implementing these principles starts with a simple plate model: half the plate non-starchy vegetables or fruit, a quarter lean protein, and a quarter complex carbohydrates, with healthy fats added in small amounts. This framework supports healthy eating habits by making it easier to plan meals and monitor portions. Prioritize fiber-rich choices, stay hydrated, and limit ultra-processed items to protect overall health and well-being.
Applying Balanced Diet Principles Across Settings to Build Healthy Eating Habits
Whether at home, at work, or on the go, applying Balanced Diet Principles helps establish healthy eating habits that endure. Through thoughtful meal planning, you can ensure variety and balance even a忙 schedule, selecting nutrient-dense options that fit personal preferences and cultural foods while supporting nutrition for health.
Use practical tools like a simple dietary journal or a weekly meal plan to track progress. By focusing on portion control and consistent meal planning, you reinforce nutrition for health and support energy, mood, sleep, and daily performance. Small, repeatable changes—such as batch-cooking, incorporating frozen vegetables, and choosing balanced snacks—add up to meaningful, lasting health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I apply Balanced Diet Principles through meal planning to support nutrition for health?
Balanced Diet Principles emphasize variety, adequacy, moderation, and balance. For meal planning, use the plate model: half the plate with non-starchy vegetables or fruit, one-quarter lean protein, one-quarter complex carbohydrates, plus small amounts of healthy fats. Plan meals weekly to ensure fiber, protein, and nutrient density, and build a grocery list around colorful vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. Batch-cook when possible, limit ultra-processed foods, stay hydrated, and practice mindful eating. This practical approach supports nutrition for health by delivering steady energy, better mood, and sustainable wellness.
What role does portion control play in Balanced Diet Principles, and how can I practice it to support healthy eating habits?
Portion control is a key tool within Balanced Diet Principles to prevent overeating and support energy balance. Use visual cues or simple measures: plate method for meals, hand-portion guides (e.g., palm-sized portions for protein, a fist for carbs, a thumb for fats). Start with a baseline portion, then adjust for activity and goals. Pre-portion snacks, read nutrition labels, and consider smaller plates to avoid oversized servings. Consistently practicing portion control reinforces healthy eating habits and helps sustain long-term health and energy.
| Key Topic | Summary | Practical Takeaways / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose and Core Idea | Nutrition is built on steady habits rather than quick fixes; balance variety and nutrient-dense foods in right amounts to support energy and long-term wellness. |
|
| Core Components | Variety, Adequacy, Moderation, Balance; Hydration; Mindful eating; Emphasis on whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and water. |
|
| Practical Steps | Plate model with emphasis on fiber and protein; plan meals; choose healthy fats; portion control; limit ultra-processed foods; stay hydrated; tailor to needs. |
|
| Settings | Apply principles at home, work or school, dining out, and on the go. |
|
| Barriers and Solutions | Time constraints; budget concerns; cravings and social situations; knowledge gaps. |
|
| Evidence and Tracking | Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins support health; track progress by energy, mood, sleep, digestion, and daily function. |
|
| Special Considerations | Tailored guidance for pregnancy, older adults, athletes, or chronic conditions. |
|
| Personal Plan | Baseline tracking; apply plate model; gradually replace ultra-processed foods; set realistic goals. |
|
Summary
Balanced Diet Principles describe a sustainable framework for nourishment that emphasizes variety adequacy moderation and balance. This descriptive overview highlights how consistent nutrient-dense food choices support energy, mood, sleep, and long-term wellness. The guide translates theory into actionable steps—plating, fiber and protein priorities, healthy fats, meal planning, and mindful portions—making healthy eating practical in everyday life. Settings such as home, work, dining out, and travel are addressed with strategies to overcome common barriers like time, budget, and cravings. By tracking progress beyond weight and tailoring guidance to individual needs, Balanced Diet Principles become a flexible, lifelong approach to health.