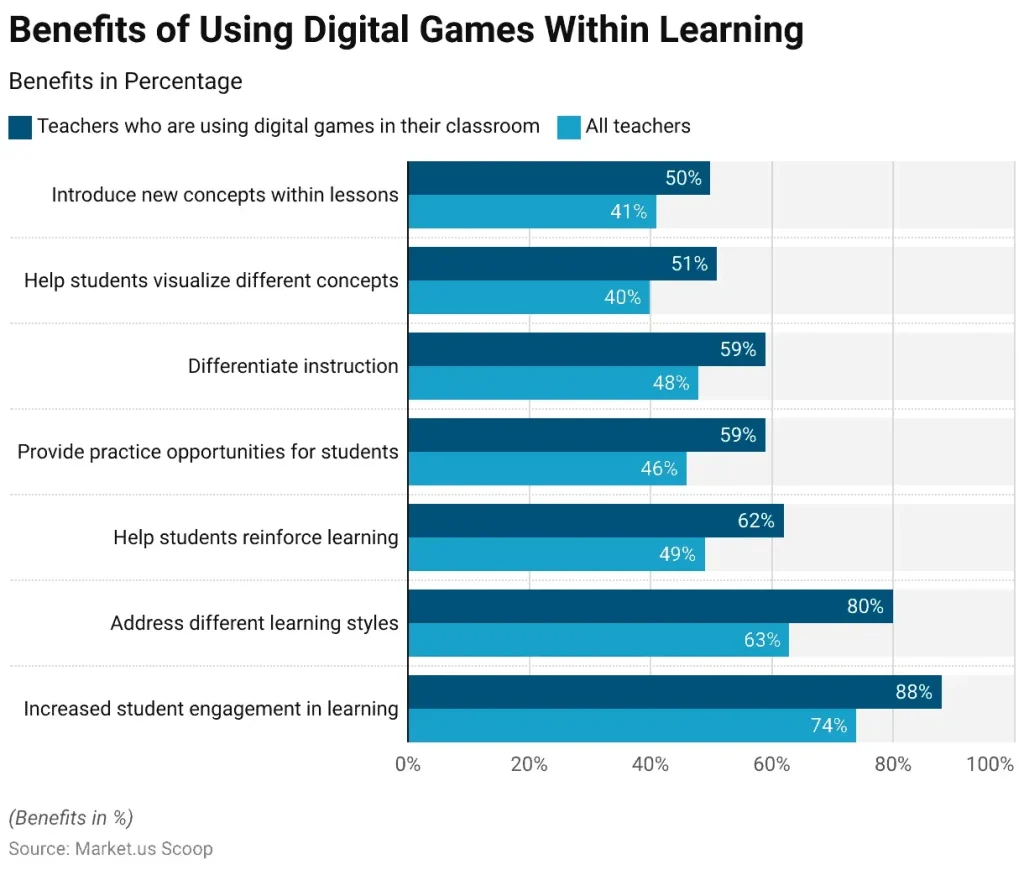
Impact of games on learning has emerged as a dynamic force shaping classrooms, corporate training rooms, and home study environments. Educators and researchers are documenting improved motivation, deeper understanding, and better transfer of skills when games are thoughtfully integrated. These tools should be aligned with standards and learning goals, while providing immediate feedback and scalable challenge. Even in collaborative settings, games encourage communication, shared problem solving, and respectful teamwork that translate beyond the screen. When designed with purpose, gamification in learning can boost focus and productivity, without sacrificing autonomy or curiosity.
Viewed through an alternative lens, this topic can be described as playful learning, game-based instruction, or interactive pedagogy that leverages rules and feedback. LSI principles encourage connecting terms such as digital simulations, experiential learning, and inquiry-driven activities to the core ideas of play-powered education. By using related concepts like educational simulations, immersive learning environments, and narrative-driven tasks, educators can broaden the conversation. In short, these semantic variations point to the same objective: harnessing structured play to deepen understanding, transfer knowledge, and build durable skills.
Impact of games on learning: How game-based strategies elevate understanding, retention, and transfer
Research into the Impact of video games on learning shows that well-chosen games can boost attention, motivation, and deep conceptual understanding. Game-based learning provides immediate feedback, clear goals, and scalable challenge, enabling learners to progress at their own pace. This aligns with the broader concept of games for education, where interactive simulations translate abstract ideas into tangible practice and support memory through spaced repetition and retrieval prompts.
Beyond cognition, the social effects of play are notable. video games and social skills develop as learners collaborate on shared tasks, negotiate roles, and provide constructive feedback. When educators design collaborative challenges around the game, learners practice communication and leadership in authentic contexts. Using gamification in learning intentionally—emphasizing autonomy, mastery, and purpose rather than mere rewards—can enhance motivation while protecting against extrinsic burnout and promoting sustained engagement. This approach also links to broader ideas of gaming and productivity in real-world settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Impact of games on learning for student outcomes, and how can teachers use games for education effectively?
The Impact of games on learning can lift engagement, deepen understanding, and improve knowledge transfer when games for education are carefully matched to learning goals and standards. To implement effectively, select evidence-based titles, align gameplay with curricular objectives, provide clear objectives and feedback, and assess mastery through performance tasks and reflection.
How does gamification in learning and video games and social skills influence productivity and collaboration in classrooms and workplaces?
Gamification in learning and video games and social skills development can boost collaboration, communication, and practical problem-solving by offering structured challenges and timely feedback. To maximize productivity and transfer, design collaborative game activities with clear rubrics, ensure equitable access, include debriefs that connect in-game outcomes to real-world tasks, and monitor content quality and safety.
| Aspect | Key Points | Implications / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Overview and purpose | Games can elevate learning when used thoughtfully; debates about their value have given way to a growing evidence base; when chosen and integrated thoughtfully, games can enhance understanding, retention, and life skills. | Choose games aligned with objectives; integrate into the broader instructional or training design; ensure they support curriculum standards. |
| Learning gains and engagement | Games provide immediate feedback, clear goals, and scalable challenges; failure is framed as a stepping stone to mastery; intrinsic motivation drives engagement. | Design with feedback loops and visible progress toward mastery; align activities with learning goals; track improvements. |
| Cognitive engagement and memory | Educational games turn abstract ideas into concrete tasks; spaced practice and varied contexts aid memory; narrative context and feedback reinforce learning. | Embed in the broader curriculum to support retention and transfer; provide opportunities to apply knowledge in new situations. |
| Social skills and collaboration | Cooperative and competitive scenarios foster communication, negotiation, and joint problem solving; games can build empathy, leadership, and social awareness. | Design collaborative challenges aligned with social-emotional learning goals; emphasize teamwork and constructive feedback. |
| Gamification role | Points, levels, badges, and narratives can enhance engagement and social learning; however, extrinsic motivation can backfire if not balanced. | Prioritize autonomy, mastery, and purpose; avoid over-reliance on rewards and guard against manipulation. |
| Productivity and focus | Short, well-designed game-based activities (microlearning) support skill-building and transfer to real tasks; onboarding and scalable continuing education benefit workplaces. | Use adaptive difficulty and reflective prompts; connect game outcomes to real-world performance and productivity goals. |
| Implementation approaches | Start with clear outcomes; ensure accessibility and equity; curate a balanced mix of content-focused, simulation, and collaborative games; integrate with traditional instruction and assessment. | Plan deliberately, provide supports, and ensure alignment with instructional or training objectives. |
| Measuring impact and quality | Assessment should map to outcomes using tests, performance tasks, and portfolios; rubrics should evaluate problem-solving, collaboration, and transfer. | Regular content reviews and bias checks maintain alignment with standards and accessibility. |
| Challenges and considerations | Screen time, content quality, and equity require careful management; not all games are equally educational; design, safety, and privacy matter. | Conduct due diligence; use learning design expertise; position games as an enhancement, not a substitute for instruction; set boundaries. |
| Benefits for stakeholders | Engagement, motivation, and mastery for learners; flexible pathways for diverse students; improved productivity and organizational performance in workplaces. | Adopt tools that meet diverse needs, monitor outcomes, and align with long-term learning and performance goals. |
Summary
Impact of games on learning is not a one-size-fits-all claim but a nuanced approach to education and development. When integrated with clear objectives, well-designed games can elevate understanding, deepen retention, and sharpen social skills while boosting motivation and productivity. Success depends on thoughtful selection, alignment with standards, and ongoing assessment to ensure that game-based experiences support desired outcomes. This requires deliberate pedagogy, accessible design, and continuous reflection to adapt games to diverse learners and contexts. By embracing games for education, teachers, trainers, and leaders can unlock engaging pathways for learners to apply knowledge, collaborate effectively, and develop transferable skills for success in school, work, and life.